It’s All in the Applications
TNSR provides stellar packet per second and gigabit per second performance for the most demanding secure networking applications..

What is IPv4 Address Space Exhaustion?
Internet Protocol version 4 (IPv4) is a system of addresses used to identify devices on a network. IPv4 addresses are 32-bit numbers, i.e., there are 232, or just over four billion, possible addresses. When the commercial Internet began circa the mid 90’s, four billion addresses seemed enormous. But now with nearly half of the world’s population using a smartphone, and with the Internet of Things (IoT) at its infancy, IPv4 space is gone. Service providers - the purveyors of address space, must deal with this problem by evolving new IP address needs to IPv6. Still, IPv4 legacy remains so scalable address translation is needed.
This solution for IPv4 address space exhaustion is generally referred to as Carrier-grade Network Address Translation (CGN or CGNAT), as well as large-scale NAT (LSN).
Scalable, cost-effective LSN/CGN is challenging. Hardware-based solutions require sizable ternary content-addressable memory (TCAM) to manage address translation at speed. TCAM-intensive products are also expensive and difficult to scale to the levels needed. TNSR overcomes these challenges by delivering cost-effective, scalable, and high-performance CGNAT in software.

Network Address Translation
Carrier-Grade NAT
DHCP Client / Server
DNS Resolver
VRRP
CGNAT Features
Network Address Translation
Network address translation (NAT) is a method of mapping an IP address space into another by modifying network address information in the IP header of packets while they are in transit across a traffic routing device.
TNSR supports the following NAT functionality:
- Port Forwards - allows external devices access to computers on private networks by mapping an external port to an internal IP address and port
- 1:1 NAT - maps a single external IPv4 address (usually public) to a single internal IPv4 address (usually private)
- Outbound NAT - (sometimes referred to as Source NAT, Overload NAT or Port Address Translation (PAT)) changes the source address and port of packets exiting a given interface in order to 1) hide the origin of a packet, or 2) allow multiple IPv4 hosts inside a network to share one, or a limited number of, external or outside addresses on a router
- Network Prefix Translation (NPt) works similarly to 1:1 NAT but operates on IPv6 prefixes instead
Carrier-Grade NAT
Service providers around the world face a problem of IPv4 address space exhaustion. This is, of course, driving not only IPv6, but the use of address space mapping technologies that help extend the life of compute and networking equipment that are bound to IPv4 address usage.
Carrier-grade NAT (CGN or CGNAT), also known as large-scale NAT (LSN), is an approach to IPv4 network design where end sites, particularly residential networks, are configured with private network addresses that are translated to public IPv4 addresses by network address translator solutions located within the service provider’s network, permitting the sharing of small pools of public addresses among many end sites. This shifts the NAT function from the end customer network to the service provider network.
TNSR supports two technologies useful to CGNAT:
- NAT44 - maps each application flow on the customer side to the public IPv4 address and one of its TCP or UDP ports as identified by the combination of a private IPv4 address and a TCP or UDP port
- Mapping of Address and Port (MAP) - MAP is a carrier-grade IPv6 transition mechanism capable of efficiently transporting high volumes of line-rate IPv4 traffic across IPv6 networks. TNSR supports both MAP-T (which uses translation) and MAP-E (which uses encapsulation). TNSR can currently act as a Border Relay (BR) providing service to Customer Edge (CE) clients.
- Network Address Translation-Traversal (NAT-T) - the standards-based approach for IPsec encapsulation in User Datagram Protocol (UDP) to ensure that data protected by IPsec can pass through NAT without discarding packets - key for IPsec VPN connections that traverse connections where NAT is present, especially for service providers
More information can be found in our documentation.
DHCP Client / Server
A Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) Server is a network server that automatically provides and assigns IP addresses, default gateways and other network parameters to client devices. TNSR can be configured as a client or server.
More information can be found in our documentation.
DNS Resolver
A Domain Name Server (DNS) resolver receives and resolves DNS (URL to IP address) queries from web browsers and other applications.
More information can be found in our documentation.
VRRP
The Virtual Router Redundancy Protocol (VRRP) enables hosts on a LAN to make use of redundant routing platforms on that LAN without requiring more than the static configuration of a single default route on the hosts. This increases the availability and reliability of routing paths via automatic default gateway selections - via an election protocol - on an IP subnetwork. The advantage of VRRP is high availability without requiring configuration of dynamic routing or router discovery protocols on every end-host.
More information can be found in our documentation.
Who Needs CG-NAT?
Service Providers
CGNAT solutions are necessary for telecom companies, Internet Service Providers (ISPs), Wireless Internet Service Providers (WISPs).

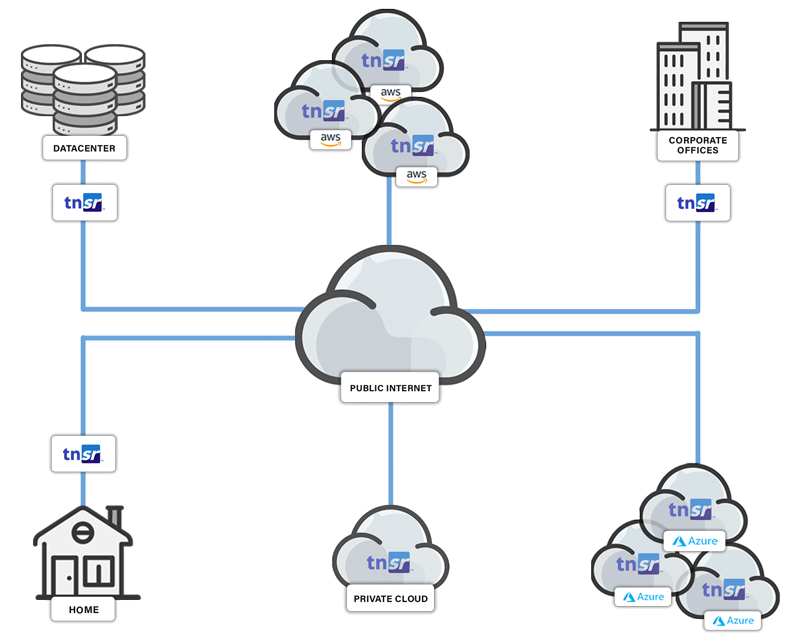
Where Should CG-NAT Be Deployed?
CG-NAT typically operates on border routers.
What Makes TNSR a Great IPv4 Solution?
High Throughput
- Leverages Vector Packet Processing (VPP) to improve packet processing performance one to two orders of magnitude over kernel-based processing solutions
- Performance scales as connection bandwidth increases, and as packet sizes fall from jumbo frames to IMIX to pure 64 byte traffic - driven by the most demanding applications
Feature Rich
- NAT44 - maps each customer side application flow to a public IPv4 address and TCP/UDP port
- Supports Mapping of Address and Port (MAP) - both MAP-T (translation) and MAP-E (encapsulation)
- Network Address Translation-Traversal (NAT-T) - ensures data protected by IPsec can pass through NAT without discarding packets
Easily Scalable
- Scale out with additional appliances, virtual machines or cloud instances
- Scale up within each software instance without the need for highly expensive, capacity-limited Ternary Content-Addressable Memory (TCAM)
Excellent overall solution value
- Unbeatable price-performance for address space management functions
- No feature, bandwidth or other incremental licensing charges
- Leverages the most advanced open source technologies
- Commercial subscriptions include the full benefit of seasoned global support specialists

%201.png?width=302&name=Netgate%20Logo%20PMS%20(horizontal)%201.png)
